Osteoarthritis of the knee joint, or gonarthrosis, occupies a leading position in the incidence of osteoarthritis.This is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of a chronic nature that affects all elements of the joint.The cartilage begins to deteriorate, changes occur in the capsule, synovial membrane, ligament apparatus and adjacent bone structures.The disease also has an additional name - gonarthrosis.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis in the knee joint
They can be more or less pronounced and completely dependent on the scene.
The pain syndrome at the beginning of the disease is almost imperceptible, but as the disease progresses, it intensifies.The first phase is characterized by tiredness in the legs and reduced joint mobility, usually in the morning.
In the second stage of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the pain is accompanied by a crunching sound that accompanies movement and limited mobility.
The third stage of the disease has a more serious clinical picture - the pain does not go away even at rest, severe deformation is noticeable, and the joints lose their functions.In addition, the gait changes.
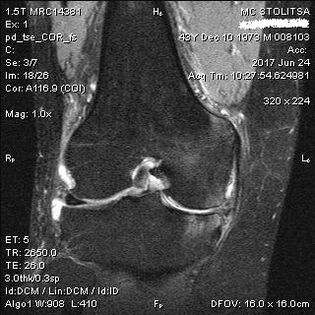
Causes of osteoarthritis in the knee joint
- Various injuries - broken bones, sprains and torn ligaments, bruises and others;
- excessive stress on the legs, most often among professional athletes and people who are forced to stand on their feet for a long time during the working day;
- various metabolic disorders that lead to the deposition of salts in the joint cavities;
- previous surgical operations to remove the meniscus;
- excess weight and obesity of any degree, which causes excessive stress on the legs;
- inflammatory processes in joint tissue - arthritis of various types.
Diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in the knee joint
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis in the knee joint takes place in the office of a rheumatologist or orthopedist.The doctor examines the affected joint, palpates it, listens to complaints and asks additional questions.Performs several tests – for example, asking the patient to bend the leg or walk a few steps.Then, if it is necessary to clarify the stage of the disease or the nature of pathological changes, he will refer you to further examinations.For example, for computed tomography or radiography.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint is often complex, aimed at eliminating pain and restoring cartilage, ligaments and joint functions.
To reduce pain, anti-inflammatory drugs, creams and rubs are used.To protect joint tissue - chondoprotectors.Sometimes hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Physiotherapy procedures and therapeutic exercises aimed at activating blood circulation in the joint area and strengthening the surrounding muscles are effective.
If the changes are irreversible, surgical treatment is prescribed - prostheses.
Prevention of osteoarthritis in the knee joint
- Eat right: your diet must contain a sufficient amount of microelements, protein and vitamins;
- avoid excessive loading of the knee joint and its traumatic lesions;
- lead an active healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits;
- timely treat all diseases and pathologies that can provoke the appearance of arthrosis;
- control your body weight and prevent obesity.

















































